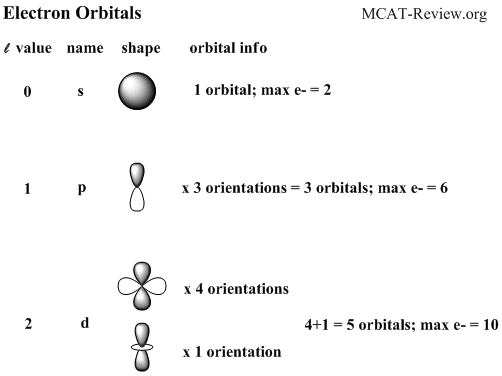
This page shows the electron configurations of the neutral gaseous atoms in their ground. If we use an orbital filling diagram, we have to count arrows. This means that every atom of potassium has 19 protons in its nucleus. These orbitals have different shapes (e.g. The orbital notation for boron is shown.
The common shorthand notation is to refer to the noble gas core, rather than write .
The orbital notation for boron is shown. • to complete an orbital diagram using arrows to represent electrons . This principle obliges the filling in of electrons in the lowest energy subshell. These orbitals have different shapes (e.g. The common shorthand notation is to refer to the noble gas core, rather than write . Group 18 element (noble gas), has a complete shell. If we use an orbital filling diagram, we have to count arrows. This means that every atom of potassium has 19 protons in its nucleus. Write the noble gas symbol in parentheses to start its electronic configuration. The following table summarizes the ground state electron configuration of the first 20 elements on the periodic table. Now, find the atomic number of the first noble gas in the periodic table. To determine the identity of an element from its electron configuration. S, p, d, f and so on are the names given to the orbitals that hold the electrons in atoms.
The chart lists elements in order of atomic number. This means that every atom of potassium has 19 protons in its nucleus. To determine the identity of an element from its electron configuration. The orbital notation for boron is shown. S, p, d, f and so on are the names given to the orbitals that hold the electrons in atoms.
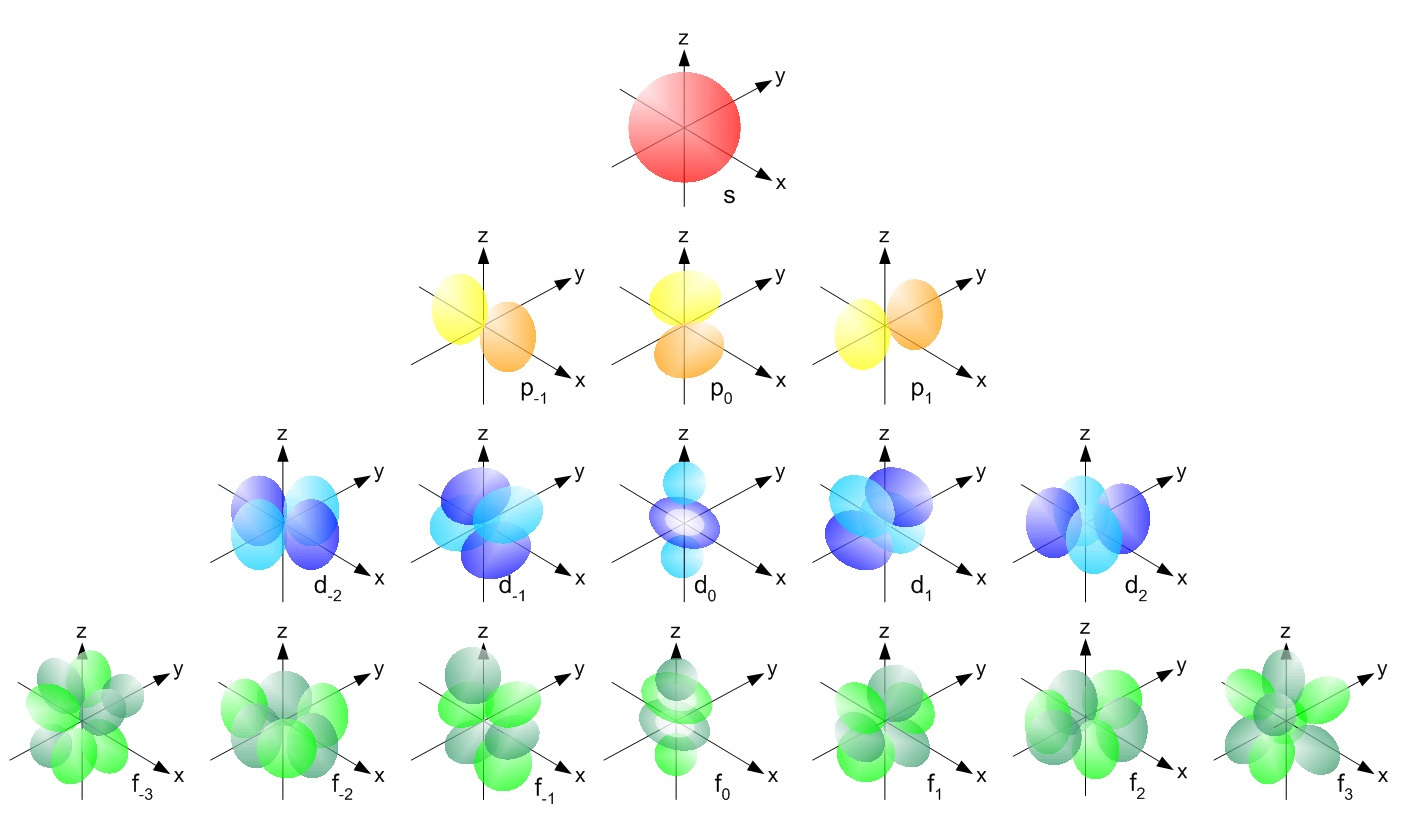
To write the electron configuration, we follow aufbau principle.
The superscripts add up to the atomic . Write the noble gas symbol in parentheses to start its electronic configuration. • to complete an orbital diagram using arrows to represent electrons . This page shows the electron configurations of the neutral gaseous atoms in their ground. Use electron configuration notation to indicate the electron configuration of an atom. Now, find the atomic number of the first noble gas in the periodic table. To write the electron configuration, we follow aufbau principle. S, p, d, f and so on are the names given to the orbitals that hold the electrons in atoms. These orbitals have different shapes (e.g. Potassium's atomic number is 19. Each method has its own purpose and each has its own drawbacks. The chart lists elements in order of atomic number. The common shorthand notation is to refer to the noble gas core, rather than write .
The following table summarizes the ground state electron configuration of the first 20 elements on the periodic table. This page shows the electron configurations of the neutral gaseous atoms in their ground. The common shorthand notation is to refer to the noble gas core, rather than write . Now, find the atomic number of the first noble gas in the periodic table. • to complete an orbital diagram using arrows to represent electrons .
This means that every atom of potassium has 19 protons in its nucleus.
This principle obliges the filling in of electrons in the lowest energy subshell. Each method has its own purpose and each has its own drawbacks. This means that every atom of potassium has 19 protons in its nucleus. S, p, d, f and so on are the names given to the orbitals that hold the electrons in atoms. Potassium's atomic number is 19. The common shorthand notation is to refer to the noble gas core, rather than write . • to complete an orbital diagram using arrows to represent electrons . The following table summarizes the ground state electron configuration of the first 20 elements on the periodic table. In a neutral atom, the number of . The chart lists elements in order of atomic number. Use electron configuration notation to indicate the electron configuration of an atom. To write the electron configuration, we follow aufbau principle. The order of the orbitals being filled can be determined by looking at the orbital chart below.
Get Spdf Notation Chart Pics. This principle obliges the filling in of electrons in the lowest energy subshell. Potassium's atomic number is 19. This page shows the electron configurations of the neutral gaseous atoms in their ground. Group 18 element (noble gas), has a complete shell. To write the electron configuration, we follow aufbau principle.
If we use an orbital filling diagram, we have to count arrows spdf chart. To write the electron configuration, we follow aufbau principle.